常用命令
lpush/lpushx/rpush/rpushx key value
lpop/rpop
rpoplpush source destination
lrem key count value //删除count个value
llen key //key中所有数据个数
lindex key index //查询索引为index的数据
linsert key before/after pivot value //在pivot前或者后插入value
lset key index value //将索引为index的元素设置为value
lrange key start stop //返回start和stop之间的元素
ltrim key start stop //修剪list,保留start和stop之间的元素
brpop/blpop/brpoplpush key timeout //阻塞式弹出
可以总结下list命令的特点
- list可以认为是有序的插入,左边是列表的头,右边是列表的尾。所以一般使用lpush/rpop
- rpoplpush src dst,从src中弹出,进入到dst中。当src和dst是一个同一个list的时候,表示对list元素进行旋转
为什么以及如何选用quicklist
对于list这种数据结构我们通常将它应用在队列中,按顺序插入和弹出,那么对于pop和push操作,时间复杂度都是O(1);对于中间元素的操作比如lindex,linsert,lset,时间复杂度都是O(N)。这符合双向链表的特点,实际上redis3.2之前,list的底层结构就是用linkedlist来实现的,linkedlist是标准的双向链表,基本上含有pre,next,data这三个元素,但是我们直到,list会被用来存储很长的元素,当元素个数高达十万到百万的时候,linkedlist这种标准的双向链表很耗费空间的,因为每一个元素都包含pre和next指针。在redis3.2之后,list底层统一用quicklist来实现,我们看下quicklist.c文件中对quicklist的注释
A doubly linked list of ziplists
quicklist就是ziplist的双向链表。quicklist的元素不是单一的一个元素了,而是一个ziplist。前面我们也分析过ziplist的结构,是一个按顺序排列的内存连续的列表。比如我们的list有12个元素,quicklist含有3个节点(ziplist),每个ziplist再包括4个元素,这样就解决一部分linkedlist占用内存太多的问题,那随之而来的就是我们如何分配quicklist节点数以及每个节点所含的元素个数,在两个极端的话就会出现以下问题
- quicklist的节点数过多,导致每个ziplist的元素过少,quicklist会逐渐转化为linkedlist,这会使插入问题变简单,但是内存占用过多
- quicklist的节点数过少,导致每个ziplist的元素过多,quicklist会逐渐转化为ziplist,解决了内存占用过多的问题,但是对于元素很多的ziplist执行插入操作将会移动分配太多的内存空间,降低效率。
所以,quicklist具体分配多少个节点,每个节点包含多少个元素根据具体的场景选择不同的方案,这里用到了redis的一个配置
# Lists are also encoded in a special way to save a lot of space.
# The number of entries allowed per internal list node can be specified
# as a fixed maximum size or a maximum number of elements.
# For a fixed maximum size, use -5 through -1, meaning:
# -5: max size: 64 Kb <-- not recommended for normal workloads
# -4: max size: 32 Kb <-- not recommended
# -3: max size: 16 Kb <-- probably not recommended
# -2: max size: 8 Kb <-- good
# -1: max size: 4 Kb <-- good
# Positive numbers mean store up to _exactly_ that number of elements
# per list node.
# The highest performing option is usually -2 (8 Kb size) or -1 (4 Kb size),
# but if your use case is unique, adjust the settings as necessary.
list-max-ziplist-size -2
这个配置指定了每一个ziplist的字节大小或者元素个数。当配置为-5到-1的时候,指定了ziplist的最大字节数。redis默认配置为-2,表明ziplist最大为8Kb。当这个配置为正数的,指定了ziplist最多的元素个数。
我们将list应用到队列的时候,通常只需要在两端处push和pop元素,中间的元素一般操作时比较少,也比较耗性能,通过配置,redis可以对中间的元素进行压缩,从而进一步的提升内存利用率。当需要的时候就进行解码,不需要的时候就进行压缩。
# Lists may also be compressed.
# Compress depth is the number of quicklist ziplist nodes from *each* side of
# the list to *exclude* from compression. The head and tail of the list
# are always uncompressed for fast push/pop operations. Settings are:
# 0: disable all list compression
# 1: depth 1 means "don't start compressing until after 1 node into the list,
# going from either the head or tail"
# So: [head]->node->node->...->node->[tail]
# [head], [tail] will always be uncompressed; inner nodes will compress.
# 2: [head]->[next]->node->node->...->node->[prev]->[tail]
# 2 here means: don't compress head or head->next or tail->prev or tail,
# but compress all nodes between them.
# 3: [head]->[next]->[next]->node->node->...->node->[prev]->[prev]->[tail]
# etc.
list-compress-depth 0
0表示所有节点均不压缩;1表示head和tail节点不压缩,其余节点均进行压缩。两端的节点总是不压缩以提高push和pop操作的效率。节点压缩采用的LZF压缩算法。
quicklist的数据结构
在quicklist.h中定义了quicklist的数据结构
/* quicklist is a 40 byte struct (on 64-bit systems) describing a quicklist.
* 'count' is the number of total entries.
* 'len' is the number of quicklist nodes.
* 'compress' is: -1 if compression disabled, otherwise it's the number
* of quicklistNodes to leave uncompressed at ends of quicklist.
* 'fill' is the user-requested (or default) fill factor.
* 'bookmakrs are an optional feature that is used by realloc this struct,
* so that they don't consume memory when not used. */
typedef struct quicklist {
quicklistNode *head;
quicklistNode *tail;
unsigned long count; /* total count of all entries in all ziplists */
unsigned long len; /* number of quicklistNodes */
int fill : QL_FILL_BITS; /* fill factor for individual nodes */
unsigned int compress : QL_COMP_BITS; /* depth of end nodes not to compress;0=off */
unsigned int bookmark_count: QL_BM_BITS;
quicklistBookmark bookmarks[];
} quicklist;
/* Node, quicklist, and Iterator are the only data structures used currently. */
/* quicklistNode is a 32 byte struct describing a ziplist for a quicklist.
* We use bit fields keep the quicklistNode at 32 bytes.
* count: 16 bits, max 65536 (max zl bytes is 65k, so max count actually < 32k).
* encoding: 2 bits, RAW=1, LZF=2.
* container: 2 bits, NONE=1, ZIPLIST=2.
* recompress: 1 bit, bool, true if node is temporarry decompressed for usage.
* attempted_compress: 1 bit, boolean, used for verifying during testing.
* extra: 10 bits, free for future use; pads out the remainder of 32 bits */
typedef struct quicklistNode {
struct quicklistNode *prev;
struct quicklistNode *next;
unsigned char *zl;
unsigned int sz; /* ziplist size in bytes */
unsigned int count : 16; /* count of items in ziplist */
unsigned int encoding : 2; /* RAW==1 or LZF==2 */
unsigned int container : 2; /* NONE==1 or ZIPLIST==2 */
unsigned int recompress : 1; /* was this node previous compressed? */
unsigned int attempted_compress : 1; /* node can't compress; too small */
unsigned int extra : 10; /* more bits to steal for future usage */
} quicklistNode;
quicklist中定义了如下字段
- head,quicklist的头结点
- tail,quicklist的尾节点
- count,quicklist所有元素总个数,llen命令直接取的这个值
- len,quicklist的节点个数
- fill,单个节点的元素填充方式,实际就是配置项list-max-ziplist-size的值
- compress,不压缩的节点个数,就是配置项list-compress-depth的值
quicklistNode中定义了如下字段
- prev/next,每个节点的前驱和后继节点
- zl,指向ziplist结构的指针
- sz,当前ziplist占用的字节大小
- count,当前ziplist中的元素个数
- encoding,当前ziplist是否被压缩
- container,当前quicklistNode以何种结构呈现,目前都是2(ziplist)
下图表示了一个quicklist的结构
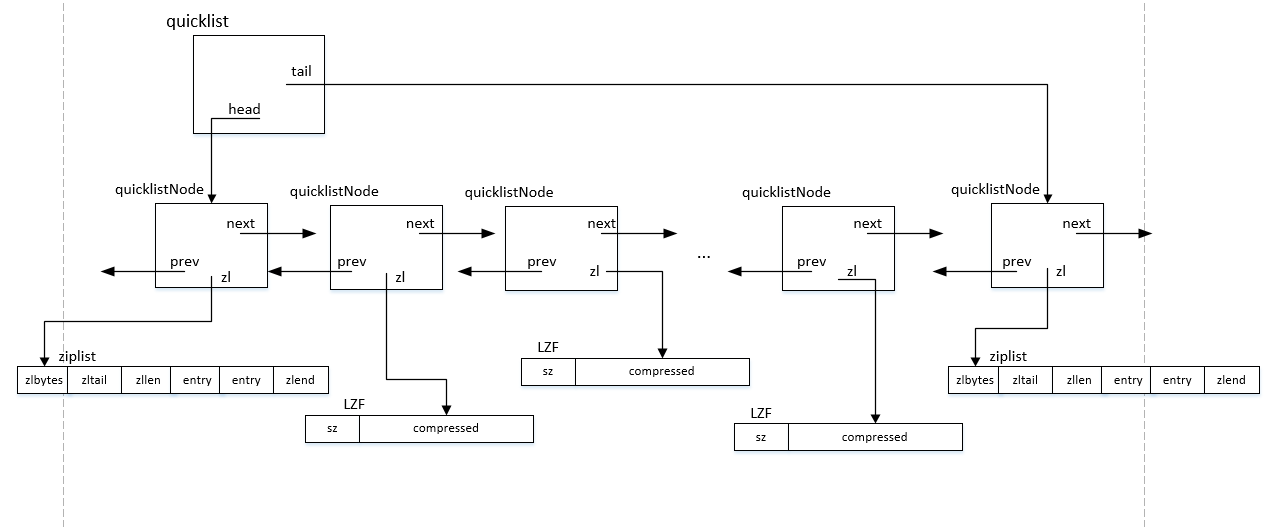
每一个quicklistNode的zl指针指向真正数据存储地址,quicklist的compress=1,表明只有head和tail两个端点是原生的ziplist结构,中间的ziplist都是被压缩的。
quicklist的常用操作及命令分析
push操作
/* Create a new quicklist.
* Free with quicklistRelease(). */
quicklist *quicklistCreate(void) {
struct quicklist *quicklist;
quicklist = zmalloc(sizeof(*quicklist));
quicklist->head = quicklist->tail = NULL;
quicklist->len = 0;
quicklist->count = 0;
quicklist->compress = 0;
quicklist->fill = -2;
quicklist->bookmark_count = 0;
return quicklist;
}
/* Add new entry to head node of quicklist.
*
* Returns 0 if used existing head.
* Returns 1 if new head created. */
int quicklistPushHead(quicklist *quicklist, void *value, size_t sz) {
quicklistNode *orig_head = quicklist->head;
if (likely(
_quicklistNodeAllowInsert(quicklist->head, quicklist->fill, sz))) {
quicklist->head->zl =
ziplistPush(quicklist->head->zl, value, sz, ZIPLIST_HEAD);
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(quicklist->head);
} else {
quicklistNode *node = quicklistCreateNode();
node->zl = ziplistPush(ziplistNew(), value, sz, ZIPLIST_HEAD);
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(node);
_quicklistInsertNodeBefore(quicklist, quicklist->head, node);
}
quicklist->count++;
quicklist->head->count++;
return (orig_head != quicklist->head);
}
/* Add new entry to tail node of quicklist.
*
* Returns 0 if used existing tail.
* Returns 1 if new tail created. */
int quicklistPushTail(quicklist *quicklist, void *value, size_t sz) {
quicklistNode *orig_tail = quicklist->tail;
if (likely(
_quicklistNodeAllowInsert(quicklist->tail, quicklist->fill, sz))) {
quicklist->tail->zl =
ziplistPush(quicklist->tail->zl, value, sz, ZIPLIST_TAIL);
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(quicklist->tail);
} else {
quicklistNode *node = quicklistCreateNode();
node->zl = ziplistPush(ziplistNew(), value, sz, ZIPLIST_TAIL);
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(node);
_quicklistInsertNodeAfter(quicklist, quicklist->tail, node);
}
quicklist->count++;
quicklist->tail->count++;
return (orig_tail != quicklist->tail);
}
执行步骤
- 如果要push的list不存在,则首先创建一个quicklist对象,包括初始化quicklist的fill和compress字段
- 创建一个redisObject,并加入到全局的dict当中
- 根据命令选择从head进行push还是tail push
- 根据quicklistNode的大小限制(byte size或者amount)判断当前ziplist是否还能继续添加元素
- 若能添加,直接向ziplist当中添加元素;若不能,创建一个新的quicklistNode,将元素插入其中。这实际上是一个纯ziplist的操作。将新创建的quicklistNode加入到quicklist当中。
- 从tail处push元素的操作与以上类似。
- 如果向quicklist中添加了新的quicklistNode,则判断是否需要将老的节点进行压缩。 由于压缩过程比较繁琐,此处不再赘述
pop操作
/* pop from quicklist and return result in 'data' ptr. Value of 'data'
* is the return value of 'saver' function pointer if the data is NOT a number.
*
* If the quicklist element is a long long, then the return value is returned in
* 'sval'.
*
* Return value of 0 means no elements available.
* Return value of 1 means check 'data' and 'sval' for values.
* If 'data' is set, use 'data' and 'sz'. Otherwise, use 'sval'. */
int quicklistPopCustom(quicklist *quicklist, int where, unsigned char **data,
unsigned int *sz, long long *sval,
void *(*saver)(unsigned char *data, unsigned int sz)) {
unsigned char *p;
unsigned char *vstr;
unsigned int vlen;
long long vlong;
int pos = (where == QUICKLIST_HEAD) ? 0 : -1;
if (quicklist->count == 0)
return 0;
if (data)
*data = NULL;
if (sz)
*sz = 0;
if (sval)
*sval = -123456789;
quicklistNode *node;
if (where == QUICKLIST_HEAD && quicklist->head) {
node = quicklist->head;
} else if (where == QUICKLIST_TAIL && quicklist->tail) {
node = quicklist->tail;
} else {
return 0;
}
p = ziplistIndex(node->zl, pos);
if (ziplistGet(p, &vstr, &vlen, &vlong)) {
if (vstr) {
if (data)
*data = saver(vstr, vlen);
if (sz)
*sz = vlen;
} else {
if (data)
*data = NULL;
if (sval)
*sval = vlong;
}
quicklistDelIndex(quicklist, node, &p);
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
操作描述如下
- 首先找到要pop的quicklistNode,要么是head,要么是tail节点
- 根据pop的位置,定位到当前ziplist要pop元素的位置
- 获取要pop的元素
- 从ziplist当中删除此元素
- 如果ziplist当中没有元素了,则删除此quicklist的节点。
在list的指定位置插入
/* Insert a new entry before or after existing entry 'entry'.
*
* If after==1, the new value is inserted after 'entry', otherwise
* the new value is inserted before 'entry'. */
REDIS_STATIC void _quicklistInsert(quicklist *quicklist, quicklistEntry *entry,
void *value, const size_t sz, int after) {
int full = 0, at_tail = 0, at_head = 0, full_next = 0, full_prev = 0;
int fill = quicklist->fill;
quicklistNode *node = entry->node;
quicklistNode *new_node = NULL;
if (!node) {
/* we have no reference node, so let's create only node in the list */
D("No node given!");
new_node = quicklistCreateNode();
new_node->zl = ziplistPush(ziplistNew(), value, sz, ZIPLIST_HEAD);
__quicklistInsertNode(quicklist, NULL, new_node, after);
new_node->count++;
quicklist->count++;
return;
}
/* Populate accounting flags for easier boolean checks later */
if (!_quicklistNodeAllowInsert(node, fill, sz)) {
D("Current node is full with count %d with requested fill %lu",
node->count, fill);
full = 1;
}
if (after && (entry->offset == node->count)) {
D("At Tail of current ziplist");
at_tail = 1;
if (!_quicklistNodeAllowInsert(node->next, fill, sz)) {
D("Next node is full too.");
full_next = 1;
}
}
if (!after && (entry->offset == 0)) {
D("At Head");
at_head = 1;
if (!_quicklistNodeAllowInsert(node->prev, fill, sz)) {
D("Prev node is full too.");
full_prev = 1;
}
}
/* Now determine where and how to insert the new element */
if (!full && after) {
D("Not full, inserting after current position.");
quicklistDecompressNodeForUse(node);
unsigned char *next = ziplistNext(node->zl, entry->zi);
if (next == NULL) {
node->zl = ziplistPush(node->zl, value, sz, ZIPLIST_TAIL);
} else {
node->zl = ziplistInsert(node->zl, next, value, sz);
}
node->count++;
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(node);
quicklistRecompressOnly(quicklist, node);
} else if (!full && !after) {
D("Not full, inserting before current position.");
quicklistDecompressNodeForUse(node);
node->zl = ziplistInsert(node->zl, entry->zi, value, sz);
node->count++;
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(node);
quicklistRecompressOnly(quicklist, node);
} else if (full && at_tail && node->next && !full_next && after) {
/* If we are: at tail, next has free space, and inserting after:
* - insert entry at head of next node. */
D("Full and tail, but next isn't full; inserting next node head");
new_node = node->next;
quicklistDecompressNodeForUse(new_node);
new_node->zl = ziplistPush(new_node->zl, value, sz, ZIPLIST_HEAD);
new_node->count++;
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(new_node);
quicklistRecompressOnly(quicklist, new_node);
} else if (full && at_head && node->prev && !full_prev && !after) {
/* If we are: at head, previous has free space, and inserting before:
* - insert entry at tail of previous node. */
D("Full and head, but prev isn't full, inserting prev node tail");
new_node = node->prev;
quicklistDecompressNodeForUse(new_node);
new_node->zl = ziplistPush(new_node->zl, value, sz, ZIPLIST_TAIL);
new_node->count++;
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(new_node);
quicklistRecompressOnly(quicklist, new_node);
} else if (full && ((at_tail && node->next && full_next && after) ||
(at_head && node->prev && full_prev && !after))) {
/* If we are: full, and our prev/next is full, then:
* - create new node and attach to quicklist */
D("\tprovisioning new node...");
new_node = quicklistCreateNode();
new_node->zl = ziplistPush(ziplistNew(), value, sz, ZIPLIST_HEAD);
new_node->count++;
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(new_node);
__quicklistInsertNode(quicklist, node, new_node, after);
} else if (full) {
/* else, node is full we need to split it. */
/* covers both after and !after cases */
D("\tsplitting node...");
quicklistDecompressNodeForUse(node);
new_node = _quicklistSplitNode(node, entry->offset, after);
new_node->zl = ziplistPush(new_node->zl, value, sz,
after ? ZIPLIST_HEAD : ZIPLIST_TAIL);
new_node->count++;
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(new_node);
__quicklistInsertNode(quicklist, node, new_node, after);
_quicklistMergeNodes(quicklist, node);
}
quicklist->count++;
}
指定位置相当于在ziplist中间插入元素,
- 若要插入的ziplist元素未满,则直接向ziplist中插入元素
- 要插入的元素在当前ziplist的尾部,且下一个ziplist未满,且是after型插入,则直接将元素插入到下一个ziplist中
- 要插入的元素在当前ziplist的头部,且上一个ziplist未满,且是before型插入,则直接将元素插入到上一个ziplist中
- 若要插入的元素在尾部且下一个ziplist满,或者要插入的元素在头部且上一个ziplist满,则创建一个新的quicklistNode,并将元素插入,谈后将ziplist插入到quicklist中
- 若要插入的元素在当前ziplist的中间位置,且当前ziplist已满,则讲当前ziplist分割为两个ziplist,向其中插入元素。再向quicklist插入节点登操作。
在list端点的处的操作大多是O(1)的复杂度,中间的操作大多是O(N)的复杂度,没有特别的技巧,因为主要通过遍历完成。因为list的一个节点是一个ziplist,所以比如lindex通过索引来查找元素的时候可以快速跳过一些ziplist,加快查找的速度(有点跳表的思路)。
关于list的阻塞命令brpop的实现方式在下一篇文章说明。
参考文章
- http://zhangtielei.com/posts/blog-redis-quicklist.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/czrzchao/article/details/78991266